Polish Localization of Odoo: Invoicing, Accounting, Warehouse, Payroll
Author: Aksel Nooitgedagt, CEO at Solvti.com in collaboration with other Odoo Partners in Poland
Date: 2025-06-17
This article is intended for Solvti team members and may be published on our blog in the future if we find it valuable to share more broadly. It serves multiple purposes:
- to clarify which Polish accounting features are supported in the standard version of Odoo and which are missing,
- to explain what kind of custom development is needed and why,
- to help assess whether the standard functionality is sufficient for a given client’s needs, and if not, what additional modules or modifications are required,
- to support our internal work on developing our own Polish localization modules,
- and finally, to be used in discussions with Odoo S.A. to clearly demonstrate which features are lacking and what improvements are needed.
Accounting requirements vary across businesses, so this article is designed to guide implementation decisions based on actual client expectations and compliance needs. It assumes reader is generally familiar with Odoo Standard functionality and focuses therefor on things that are lacking in Odoo. We inform clients that it is generally possible to run accounting in Odoo in Poland. For example, at Solvti, we fully manage our accounting in Odoo—including invoicing, expenses, JPK files, and integration with the Tax Office. However, every company is different, so accounting needs are always assessed on a case-by-case basis.
The tables below are checked against Odoo Enterprise v18.
Invoicing features
Name | Description | Available in Odoo Standard | Available as customization or module | Comment | Resources |
Compliant invoice format | According to Art. 106e ust. 1 VAT act, a standard invoice must include certain fields. | Partly | We have a module for that at Solvti. Ask Jakub Wisełka for questions. | More about invoice format: | Polish VAT Act – Ustawa o podatku od towarów i usług https://isap.sejm.gov.pl/isap.nsf/download.xsp/WDU20040540535/U/D20040535Lj.pdf |
Correction invoices | Issuing and tracking correction invoices (faktura korygująca) | Partly. There is a feature called "Credit note", but it does not automatically generate the designation “FAKTURA KORYGUJĄCA” nor does it enforce Polish formal requirements for the content of the document (e.g., indicating the reason for the correction, linking to KSeF, lines before and lines after). | We have a module for that at Solvti. Ask Jakub Wisełka for questions. |
From 2022 there is no need for showing reason of correction. Also, integration with KSeF is needed, so maybe this is a good moment for us to make our module. |
Art. 106j ustawy o VAT |
Reverse Charge | Handling “odwrotne obciążenie” (reverse-charge) VAT invoices. Include annotation on sales invoices, plus register payable and receivable VAT for vendor bills. | Yes - use Fiscal Positions | N/A | Only allowed when both sides are B2B (VAT payers). | W przypadku importu usług z UE: art. 28b ustawy o VAT; w przypadku towarów: art. 17 ustawy o VAT |
Split Payment Mechanism |
Split payment (mechanizm podzielonej płatności, MPP) on sales invoices | Not as a feature, but possible to add manual notes to invoices | Not very often needed, to be honest. - The invoice is B2B (between VAT taxpayers) - The gross invoice amount exceeds 15,000 PLN - At least one item on the invoice is listed in Annex 15 of the Polish VAT Act (e.g., electronics, steel, fuels, construction services) | Ustawa o podatku od towarów i usług (VAT), w szczególności z art. 108a ust. 1a–1b tej ustawy | |
Invoice Duplicate Marking | Marking invoices as “DUPLIKAT” (duplicate) when re-issuing | No | As of April 2026 (KSeF) this won't be needed anymore. And in general, clients are not often asking for this. | ||
Fetching NBP Exchange Rate for Foreign Currency Invoices in Poland | Yes | N/A | |||
Invoice in Foreign Currency | Issuing invoices in other currencies with PLN VAT summary | Partly. VAT amount is shown in PLN, but some KSeF requirements are lacking | N/A | In Odoo 18 polish taxes are show in PLN, so this requirement should be met. And the KSeF requirements will first be needed as of April 2026 | Art. 106a–106q ustawy o VAT – możliwość wystawiania faktur w dowolnej walucie. Art. 106e ust. 11 ustawy o VAT – kwoty podatku VAT zawsze w PLN. Art. 31a ustawy o VAT – Przeliczenia dokonuje się według średniego kursu NBP z ostatniego dnia roboczego poprzedzającego dzień powstania obowiązku podatkowego |
KSeF | Electronic invoice sending/receiving via KSeF (Krajowy System e-Faktur) | No | Solvti is working on a KSeF module. Status: | From February 1, 2026, KSeF will be mandatory for businesses whose 2025 sales (including VAT) exceed PLN 200 million (large taxpayers). From April 1, 2026, all other businesses—including small, medium, micro-entrepreneurs, VAT-exempt entities, and OSS taxpayers with a Polish NIP—must use KSeF | |
JPK_FA Export | Export of sales invoices in JPK_FA (Jednolity Plik Kontrolny) format | No | As of April 2026 (KSeF) this won't be needed anymore. And in general, we didn't have a single case where it was needed until now |
Accounting features
Name | Description | Available in Odoo Standard | Available as customization or module | Comment | Resources |
Chart of accounts & taxes | Customizable chart of accounts and polish taxes | Yes | There is a module, that imports a set of accounts. It saves a lot of time to configure everything your self: | Just remember, that making changes in chart of accounts start with how they should be reported on financial statements | |
Different CIT and VAT Dates | In Poland, the VAT date of vendor bills does not necessarily need to be the same date as when the bill should be counted for Corporate Income Tax (CIT) purposes. | No | Yes |
A vendor bill might be recognized for VAT purposes in one month (based on the delivery date) but counted for CIT purposes in a different month (based on when the invoice is received and recorded in accounting books). | |
GTU Codes on Invoices | Adding GTU codes (Grupy Towarowo-Usługowe) | No | GTU codes are exclusively a Polish requirement under domestic VAT regulations. They are not used in other EU countries. They are mandatory only for sales (they do not apply to purchases). They are not placed on the invoice - they are only shown in the JPK_V7 file (JPK_V7M or JPK_V7K). They are aimed at tightening the VAT system and facilitating fiscal control | Regulation of the Minister of Finance of October 15, 2019, on the detailed scope of data in tax declarations and VAT records (Dz. U. 2019 poz. 1988). GTU codes are legally required in the JPK_V7 file for all qualifying sales transactions. Failing to report them can result in compliance issues with the Polish tax authorities. | |
Bank Synchronization & Reconciliation | Automated synchronization and reconciliation with bank accounts | Yes | N/A | Polish banks supported at 2025-05-27: | |
Automated Payment Processing | Creation of payment files for online banking and batch payments | Partially | Standard SEPA; Polish Elixir/SORBNET may require custom modules. Some modules are available on | TODO: Sprawdzić i używać w Solvti. | |
Integration with Tax Office | Possibility to send JPK files directly from Odoo to the Tax Office | No | Usefull and wished by many, but not mandatory in Poland. You can always upload the file manually to the government portal using: | ||
JPK_VAT | JPK_VAT is the Standard Audit File for VAT in Poland, an electronic XML report that details all sales and purchase VAT transactions. Nearly all active VAT-registered businesses in Poland must submit JPK_VAT files monthly or quarterly | Official module is available, but not tested in practice by us | Most often requested accounting feature in Poland | Ustawy o VAT (art. 109 i art. 99), Rozporządzenia Ministra Finansów z 2019 r., a także potwierdzany przez oficjalne komunikaty MF i KAS | |
JPK_WB | Bank Statement file in JPK structure; used by tax authorities to analyze transactions on company bank accounts | No | Not commonly requested by clients, but tax authorities may demand it during audits. Based on exported bank statements. Many banks already have export of JPK_WB | Art. 193a Ordynacji podatkowej – obowiązek przekazania organom podatkowym ksiąg i dowodów księgowych w formie JPK na ich żądanie, | |
JPK_CIT | Polish Standard Audit File for Corporate Income Tax. It is an electronic reporting format that standardizes how corporate income tax (CIT) data is submitted to the Polish tax authorities. | No | Rok podatkowy po 31.12.2024 - Podatnicy CIT z przychodami przekraczającymi 50 mln euro rocznie - Podatkowe grupy kapitałowe (PGK) Rok podatkowy po 31.12.2025 - Wszyscy podatnicy CIT zobowiązani do składania JPK_VAT (czyli czynni podatnicy VAT) Rok podatkowy po 31.12.2026 - Wszyscy pozostali podatnicy CIT, niezależnie od wielkości i formy prowadzenia działalności | Mandatory as of 2025-01-01 for .arge CIT taxpayers. 2026-01-01 for others. | |
Financial statements | Generation of official financial reports: Profit and Loss (P&L), Balance Sheet, and Cash Flow Statement according to Polish accounting standards. |
? | Theoretically the functionallity is available in Odoo, but we use custom reports from Trilab at Solvti. To be checked why. | Ustawa z dnia 29 września 1994 r. o rachunkowości |
Inventory features
Name | Description | Available in Odoo Standard | Available as customization or module | Comment | Resources |
Inventory Valuation | Automatic valuation of stock (FIFO, average, manual) |
Mostly | There were some issues with goods that were bought in other currency. VAT Act (Ustawa o VAT) Art. 31a – defines how to convert foreign currency for VAT purposes: VAT amounts must be converted using the average NBP exchange rate from the last business day before the tax obligation arises (usually the invoice date). This is important because Odoo (by default) may use the exchange rate from the invoice itself, which can lead to non-compliance in Poland. | 1. Accounting Act (Ustawa o rachunkowości) Art. 28 ust. 1 pkt 2 i 11 – defines how inventory should be valued: Inventories (materials, goods, finished products) should be valued at purchase price, cost of production, or market value (if lower). The method used must ensure true and fair presentation of the financial position. | |
Foreign Currency Valuation Issue in Odoo | When purchase invoices are issued in a foreign currency and later corrected (e.g., credit note, quantity adjustment)... | WIP | |||
JPK_MAG | Monthly inventory movement report (Jednolity Plik Kontrolny – Magazyn) | No | Required for companies using full accounting and inventory. Not used often but legally required upon request by tax authorities. |
Payroll features
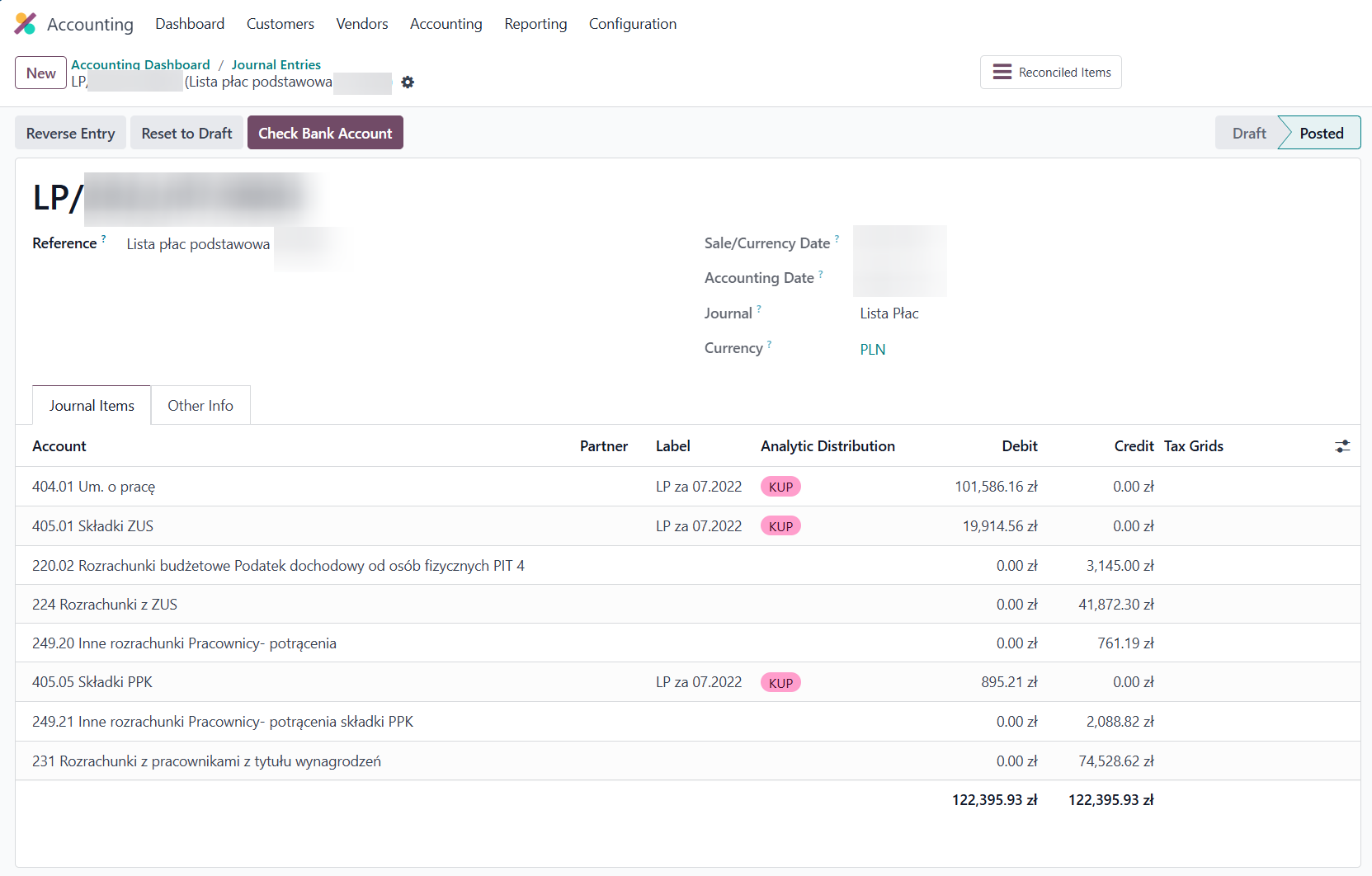
Payroll-related topics have not yet been explored in detail by our team. We’ve heard that PwC uses Odoo for payroll processing in Poland, but they have a dedicated team for this and handle payroll for several thousand employees. It’s likely that their Odoo implementation is heavily customized to support such scale and complexity.
In general, we inform our clients that we do not advise handling Payroll in Poland using Odoo. Payroll calculations are done in an external system, and then we manually record the payroll as a journal entry in Odoo and reconcile it with the corresponding payments. E.g.